HAPI Management
HAPI Management provides the ability to define and serve RESTful APIs directly from within the application code.
APIs can be declared programmatically, including request/response structures, authentication, and OpenAPI documentation.
Once activated, the system automatically generates and serves an OpenAPI specification that can be visualized using different documentation frontends.
ℹ️
HAPI Management enables full control over how APIs are exposed — including schema documentation and authentication behavior.
It integrates seamlessly with Token Management when bearer token authentication is required.
It integrates seamlessly with Token Management when bearer token authentication is required.
Functional areas
HAPI Management provides the following core functions:
API definition
- Define REST endpoints (
GET,POST,PUT,DELETE, …) programmatically - Specify request and response structures using Go generics
- Automatically generate OpenAPI documentation (
spec.json)
Request/Response mapping
- Map headers, query parameters, form data, and JSON bodies to Go structs
- Support for file uploads (
multipart/form-data) - Define typed response outputs as JSON or binary data
Authentication
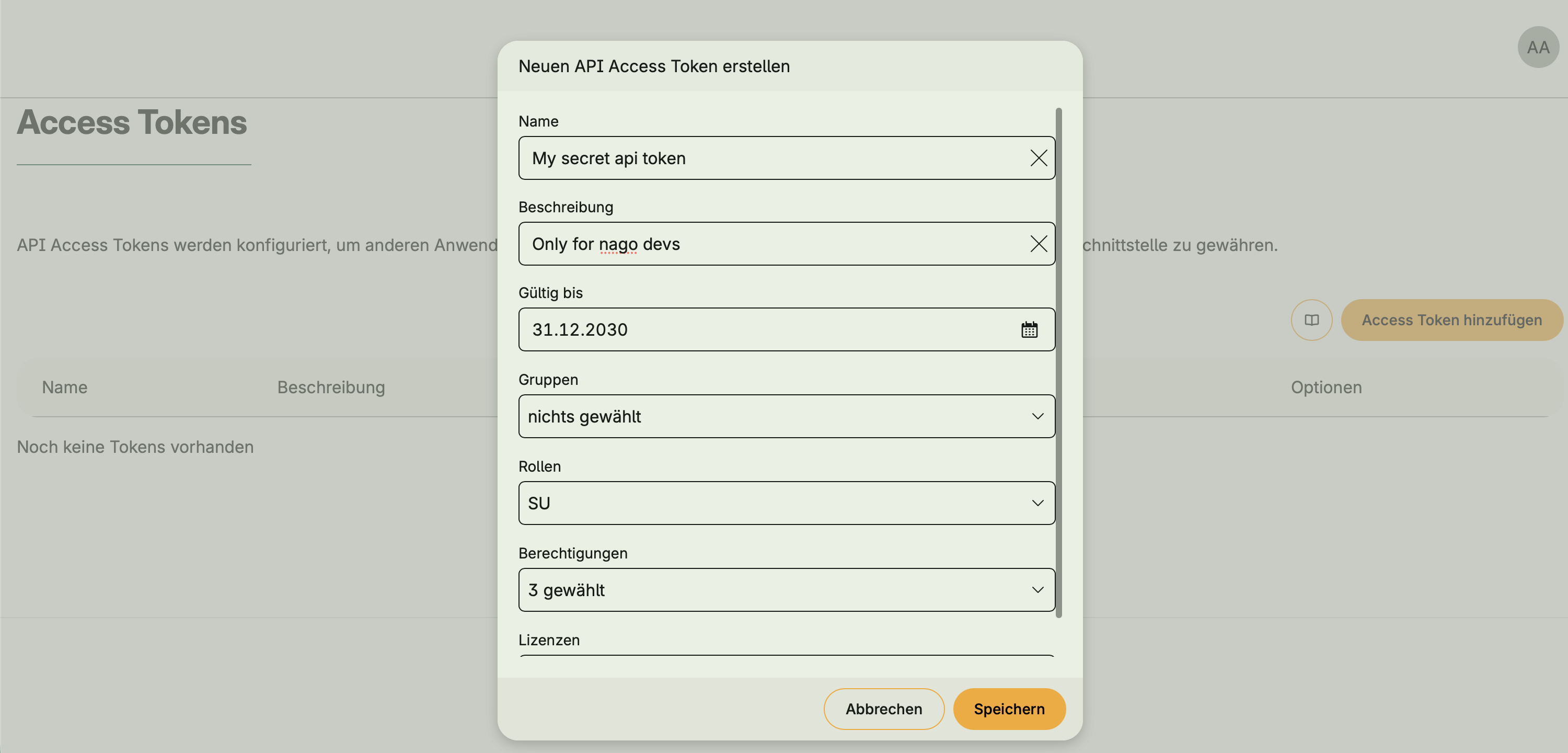
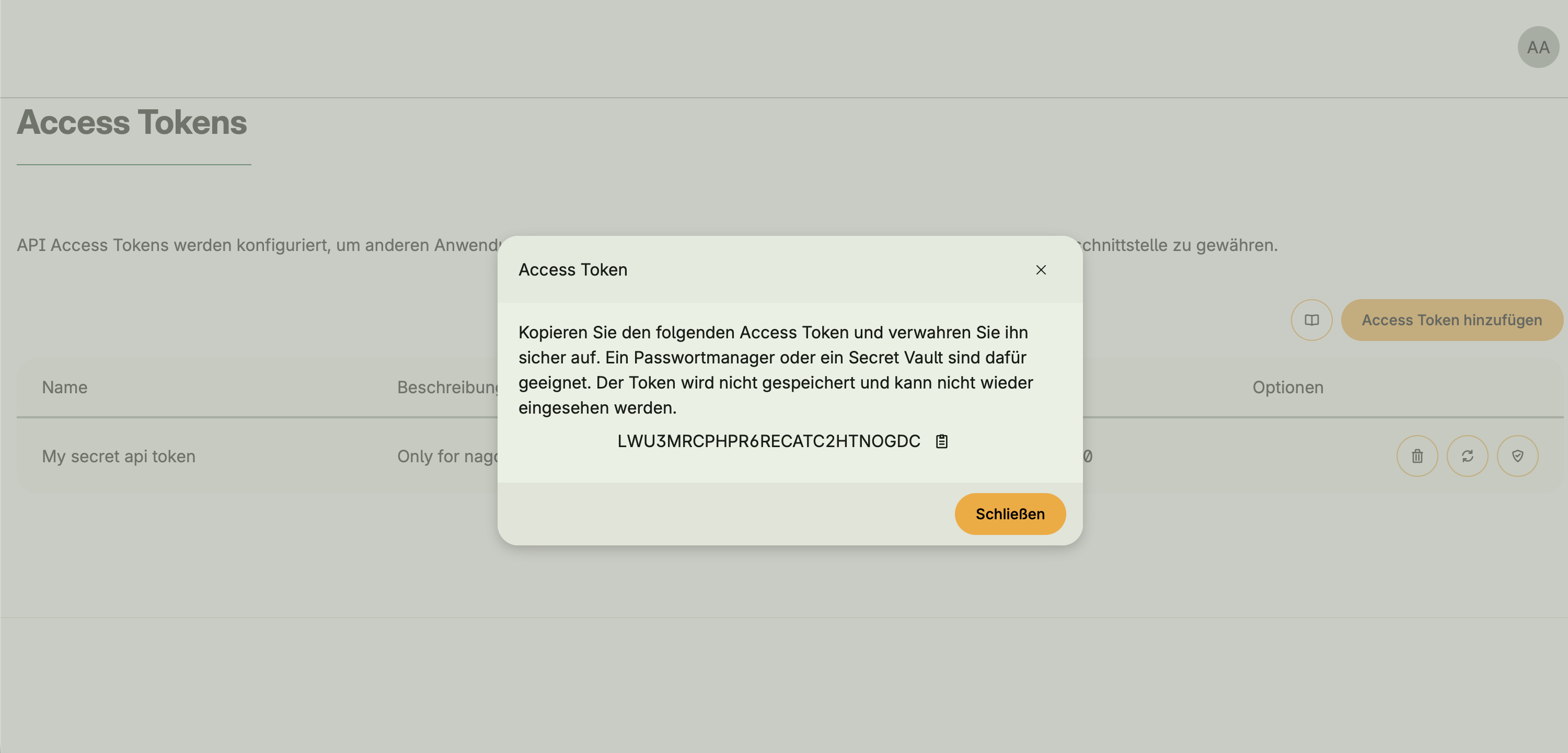
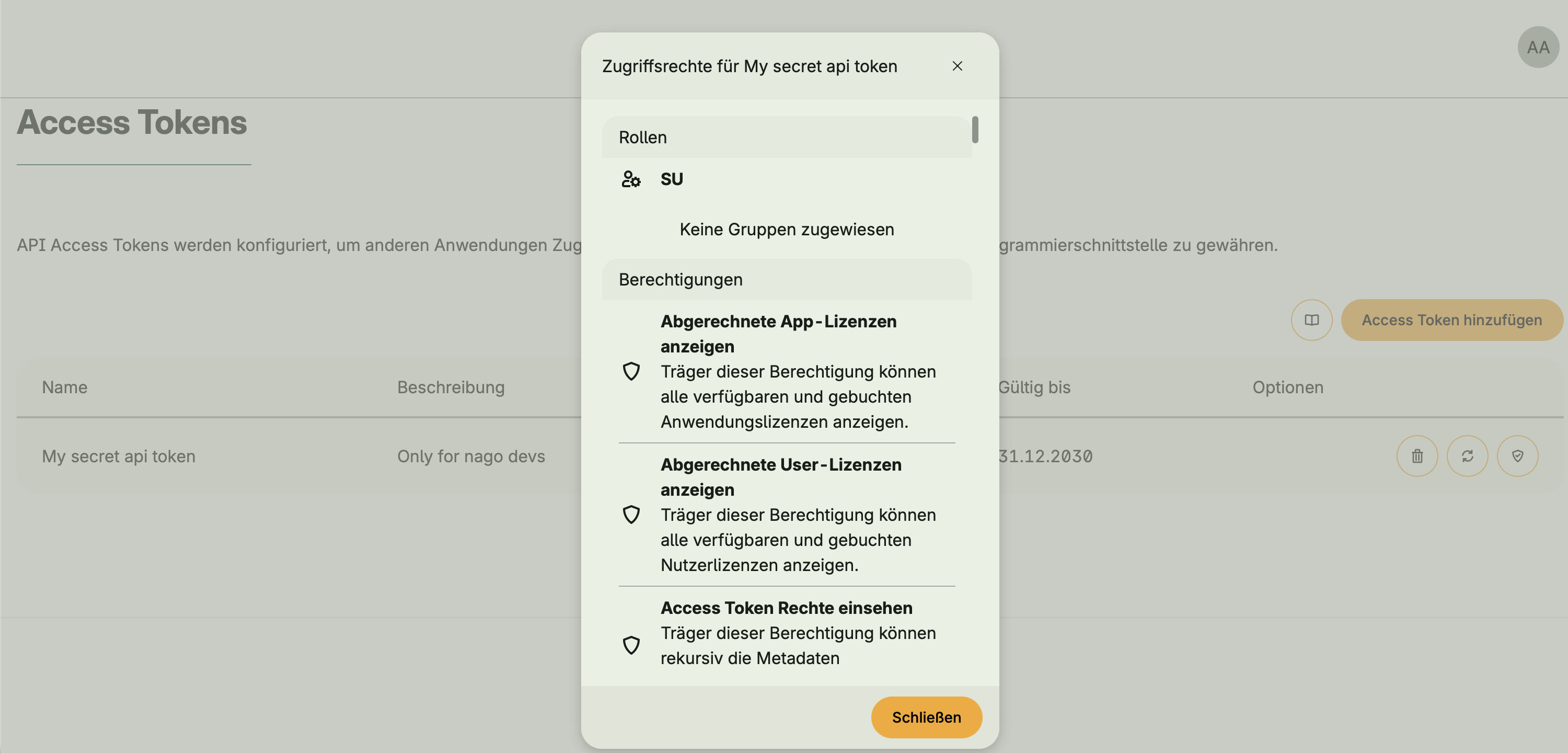
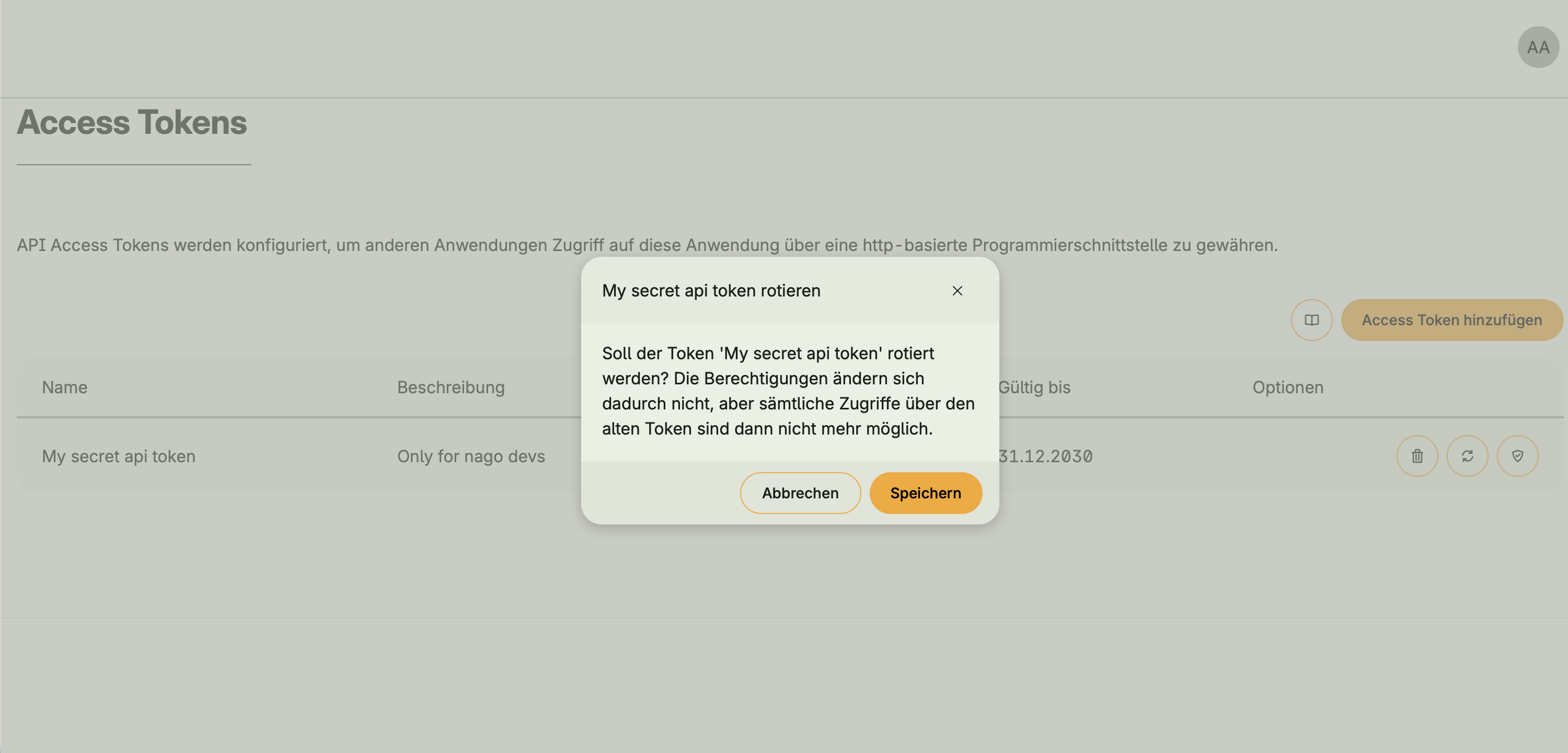
- Optional integration with Token Management via
hapi.BearerAuth - When activated, an API Access Tokens UI appears in the Admin Center
- Tokens allow external clients or users to authenticate and access protected endpoints
- Without Token Management, open APIs can still be defined, but access is unauthenticated
⚠️
While it is technically possible to expose open APIs (without authentication), this should only be done in controlled environments.
In most cases, integrating Token Management for secure access control is strongly recommended.
In most cases, integrating Token Management for secure access control is strongly recommended.
API documentation
- Serve interactive OpenAPI documentation under
/api/doc/spec.json - Choose between built-in frontends: Stoplight, Swagger, or Redocly
- The preferred frontend can be configured in the application code
⚠️
While it is technically possible to activate multiple API documentation frontends only one will be selected at runtime.
This behaviour is undefined and may lead to inconsistent results.
It is therefore strongly recommended to activate only one frontend.
This behaviour is undefined and may lead to inconsistent results.
It is therefore strongly recommended to activate only one frontend.
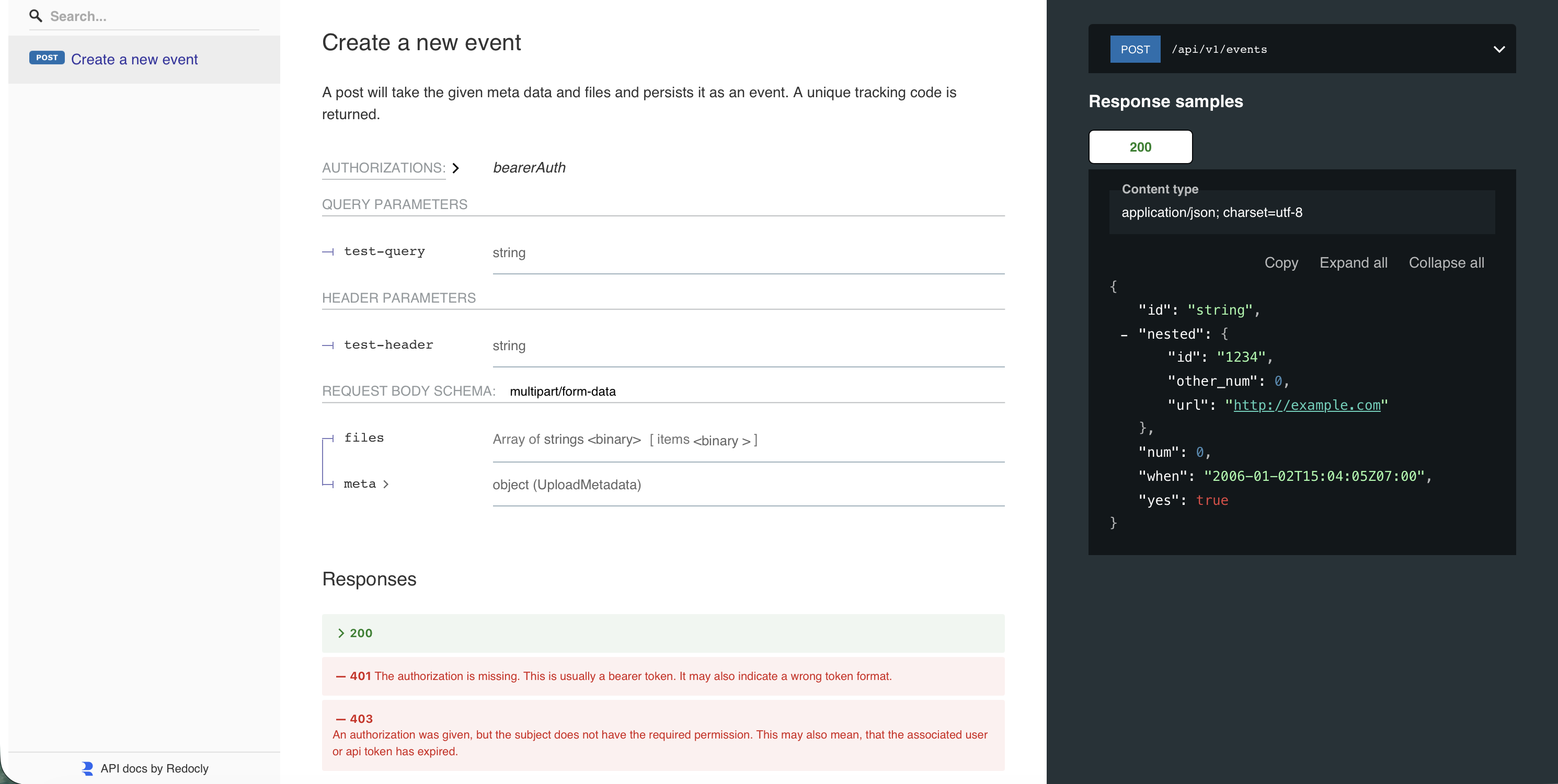
Example: Simple API endpoint
api := std.Must(cfghapi.Enable(cfg)).API
tokens := std.Must(cfg.TokenManagement())
usecases := myUsecases()
func configureMyAPI(
api *hapi.API,
tokens application.TokenManagement,
usecases myUsecases) {
type UploadRequest struct {
TestHeader string
TestQuery string
Files []*multipart.FileHeader
Subject auth.Subject
}
type UploadResponse struct {
ID string
When time.Time
}
hapi.Post[UploadRequest](api, hapi.Operation{
Path: "/api/v1/events",
Summary: "Create a new event",
Description: "Accepts metadata and files, returning a tracking ID.",
}).
Request(
hapi.BearerAuth[UploadRequest](tokens.UseCases.AuthenticateSubject, func(dst *UploadRequest, subject auth.Subject) error {
dst.Subject = subject
return nil
}),
hapi.StrFromHeader(hapi.StrParam[UploadRequest]{Name: "test-header", IntoModel: func(dst *UploadRequest, value string) error {
dst.TestHeader = value
return nil
}}),
hapi.FilesFromFormField("files", func(dst *UploadRequest, files []*multipart.FileHeader) error {
dst.Files = files
return nil
}),
).
Response(
hapi.ToJSON[UploadRequest, UploadResponse](func(in UploadRequest) (UploadResponse, error) {
if !in.Subject.HasRole("nago.dev") {
return UploadRespone{}, errors.New("invalid user")
}
// Run your use cases
id, err := usecases.Save(in.Files[0])
if err != nil {
return UploadResponse{}, err
}
return UploadResponse{ID: id + "-" + in.TestHeader, When: time.Now()}, nil
}),
)
}This example defines a simple authenticated POST endpoint that:
- Requires a bearer token for authentication
- Reads a header value from the request
- Stores the first file of the upload sent via a save use case
- Returns a JSON response with an ID and timestamp
Dependencies
Requires:
- Settings Management
- (Optional) Token Management required when bearer authentication is used
Is required by:
- None
Activation
This system is activated via:
std.Must(cfghapi.Enable(cfg))hapiManagement := std.Must(cfghapi.Enable(cfg))