Scheduler Management
Scheduler Management provides functionality to register, configure, and manage background processes (schedulers).
Schedulers are defined programmatically in the backend and automatically exposed in the Admin Center, where they can be monitored and controlled.
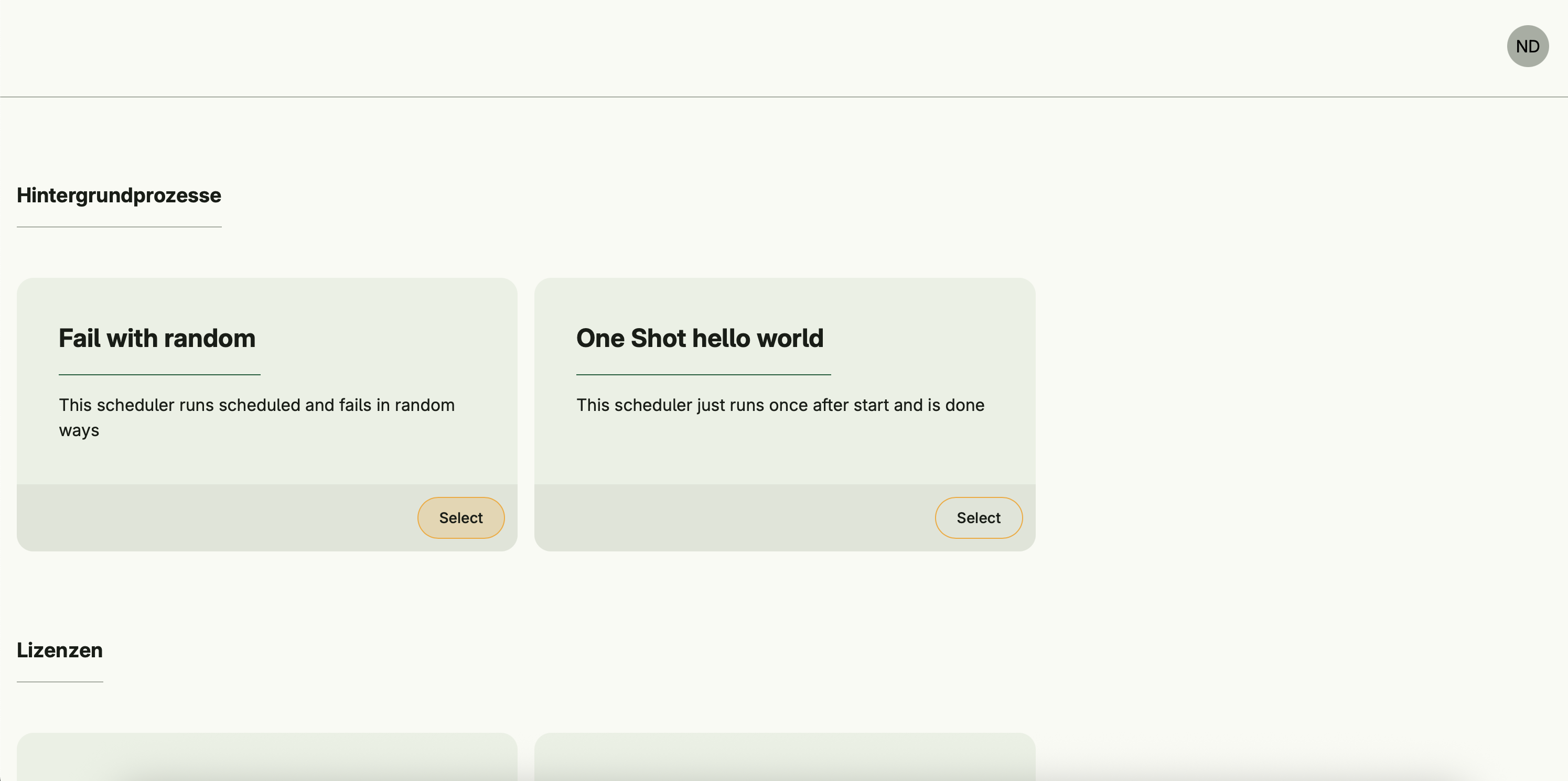
Each scheduler appears as an individual card under the Background Processes section in the Admin Center.
Authorized users can start, stop, or manually trigger schedulers, view logs, and adjust timing parameters such as delay and interval.
Functional areas
Scheduler Management provides the following key functions:
Scheduler registration
Schedulers are defined during application startup via the UseCases.Configure function.
Each scheduler specifies:
- ID, name, and description
- Kind (e.g.,
OneShot,Schedule,Manual,Cron) - Runner function containing the process logic
- Optional default settings (e.g.,
PauseTime,StartDelay) - Optional custom actions, callable from the Admin Center
Example 1: One-Shot Scheduler
scheduleManagement := option.Must(cfgscheduler.Enable(cfg))
option.MustZero(scheduleManagement.UseCases.Configure(user.SU(), scheduler.Options{
ID: "my.test.scheduler",
Name: "Hello World Job",
Description: "Runs once after startup and logs a greeting",
Kind: scheduler.OneShot,
Runner: func(ctx context.Context) error {
log := scheduler.LoggerFrom(ctx)
log.Info("Hello from scheduler")
return nil
},
}))Example 2: Scheduled recurring task
scheduleManagement := option.Must(cfgscheduler.Enable(cfg))
option.MustZero(schedulers.UseCases.Configure(user.SU(), scheduler.Options{
ID: "my.test.failure",
Name: "Fail with random",
Description: "This scheduler runs scheduled and fails in random ways",
Kind: scheduler.Schedule,
Defaults: scheduler.Settings{
StartDelay: time.Second,
PauseTime: time.Second * 10,
},
Runner: func(ctx context.Context) error {
log := scheduler.LoggerFrom(ctx)
log.Info("hello world")
for range 100 {
if ctx.Err() != nil {
return ctx.Err()
}
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 500)
r := time.Now().UnixMilli() % 1234
switch r {
case 0:
panic("ops - started to panic")
case 1:
return fmt.Errorf("failed randomly")
default:
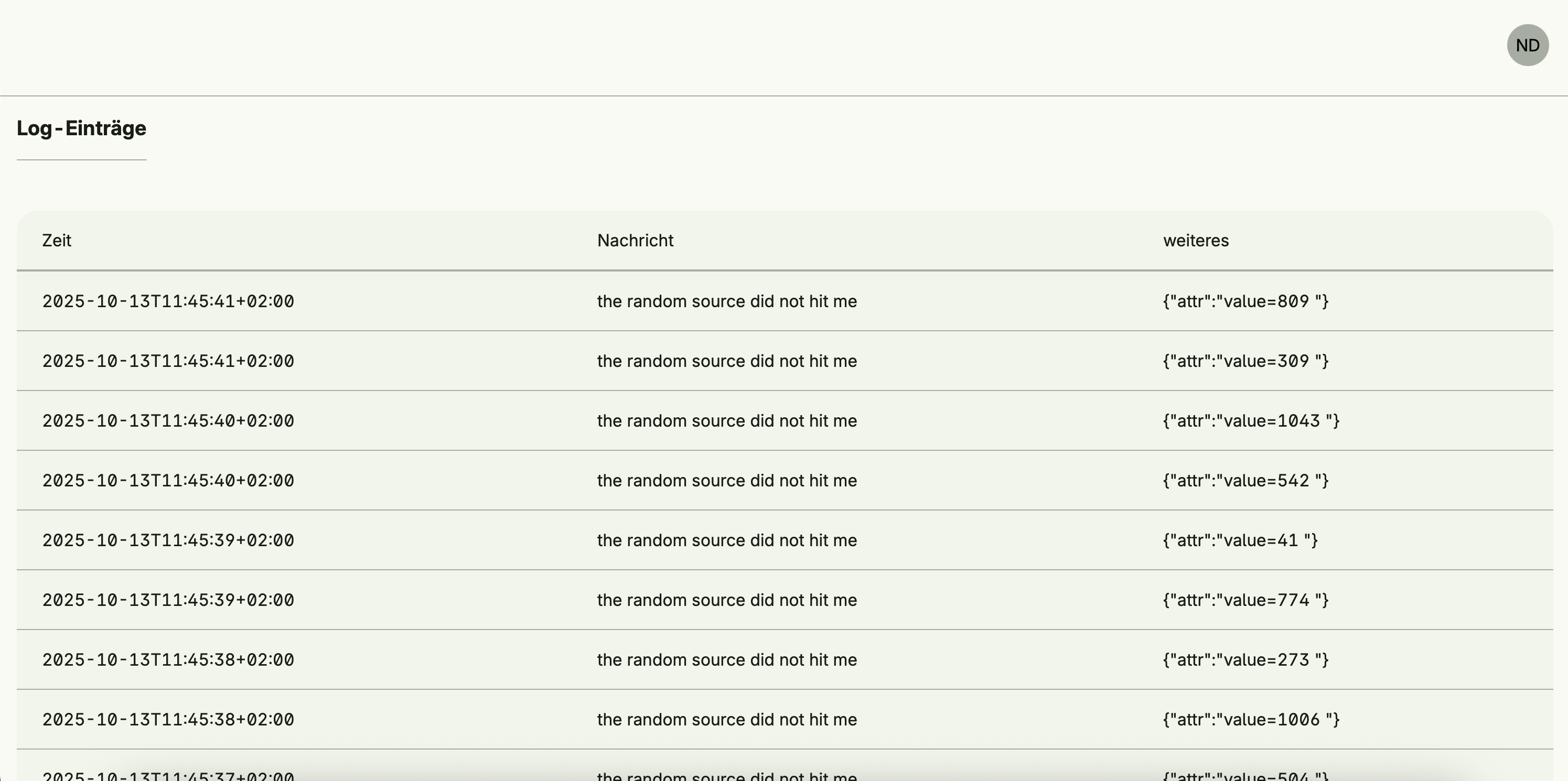
log.Info("the random source did not hit me", "value", r)
}
}
return nil
},
}))Scheduler control and monitoring
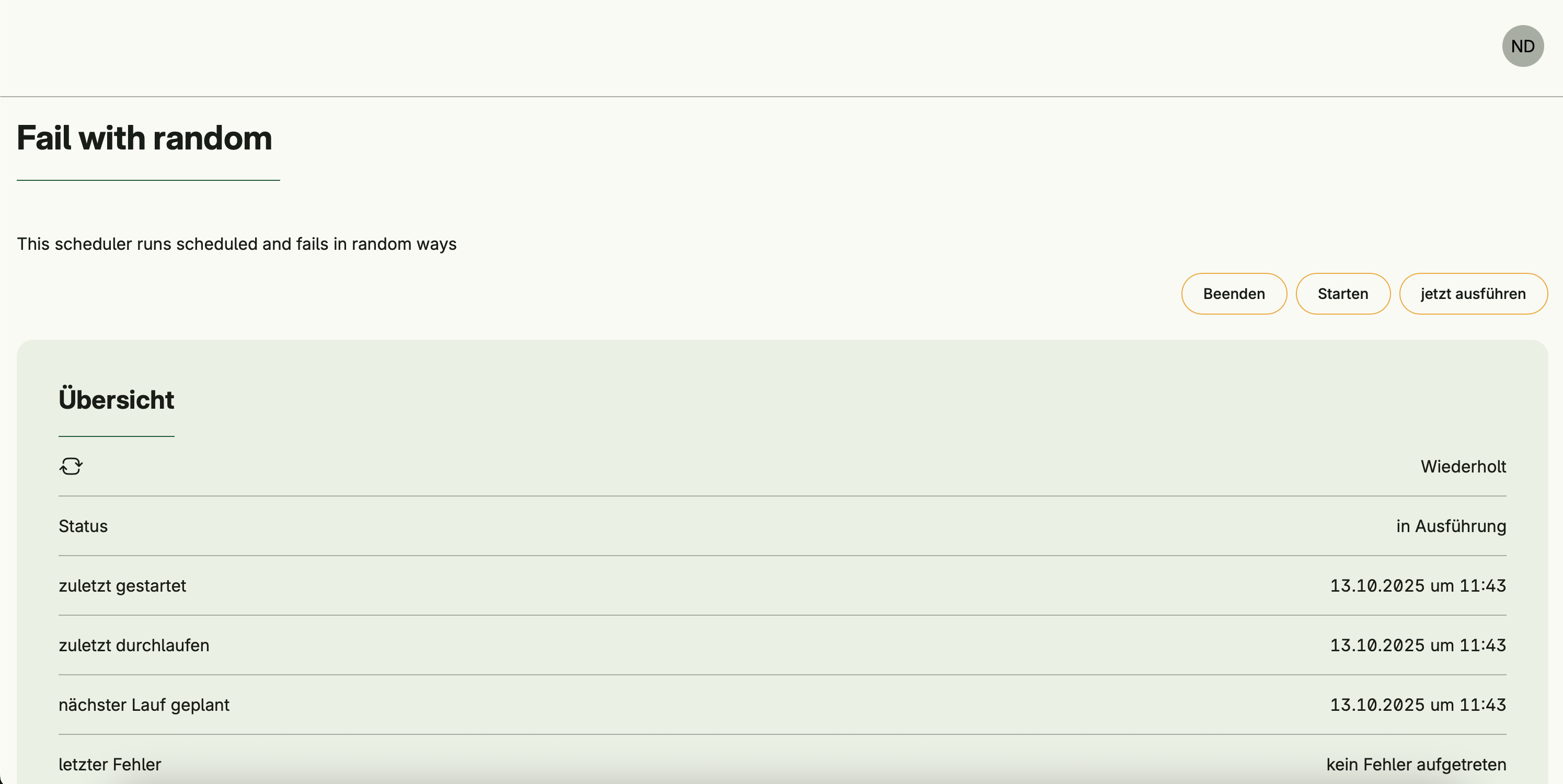
In the Admin Center UI, each configured scheduler exposes:
- Current state: Running, Paused, Disabled, or Stopped
- Timestamps: last started, last completed, next planned run
- Execution logs with timestamps, levels, and structured metadata
- Manual actions: Start, Stop, Execute Now
- Timing configuration: Adjust delay or pause intervals between runs
Schedulers can run:
- Once after startup (OneShot)
- On a fixed interval (Schedule)
- Manually triggered only (Manual)
- On a cron-like daily schedule (Cron)
Dependencies
Scheduler Management operates independently and does not depend on other systems.
Activation
This system is activated via:
schedulerManagement := std.Must(cfgscheduler.Enable(cfg))