Secret Management
The Secret Management system is responsible for storing, managing, and controlling access to sensitive data such as passwords, API keys, and configuration details for external systems (e.g., SMTP servers).
It ensures that all stored information is encrypted and can be shared securely with other users or groups within the platform.
Typical workflows include:
- Creating new secrets
- Updating existing secrets
- Deleting secrets
- Sharing secrets with specific users or groups
SMTP server
Functional areas
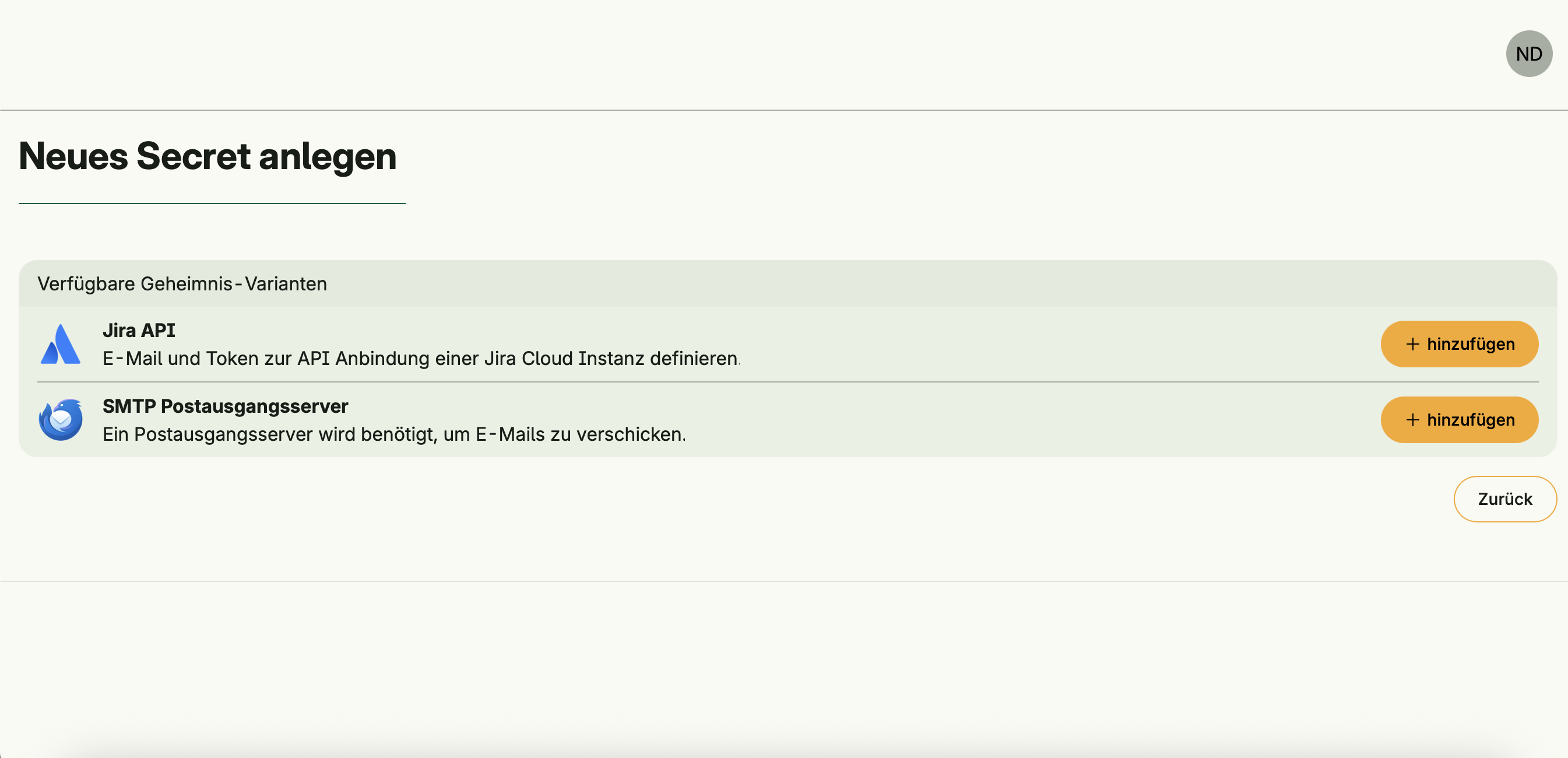
Secret Management operates within a single interface displaying all stored secrets.
Each secret is defined by its type in the source code, which determines its fields and behavior.
To add a new secret type, a developer must implement the secret.Credentials interface and add it to the Enum declaration.
package secret
type Credentials interface {
GetName() string
Credentials() bool
IsZero() bool
}var _ = enum.Variant[Credentials, MySecret]()Examples:
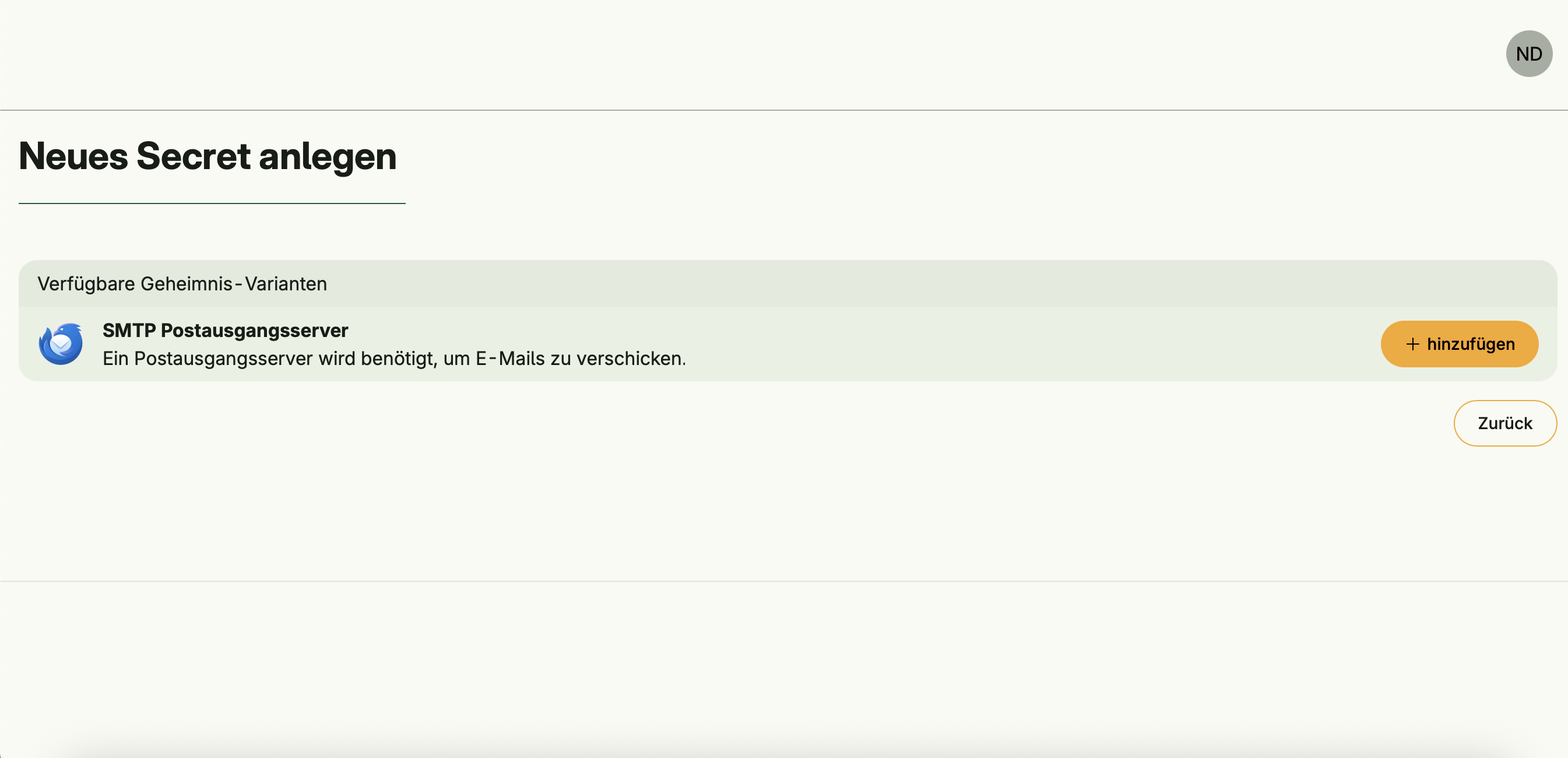
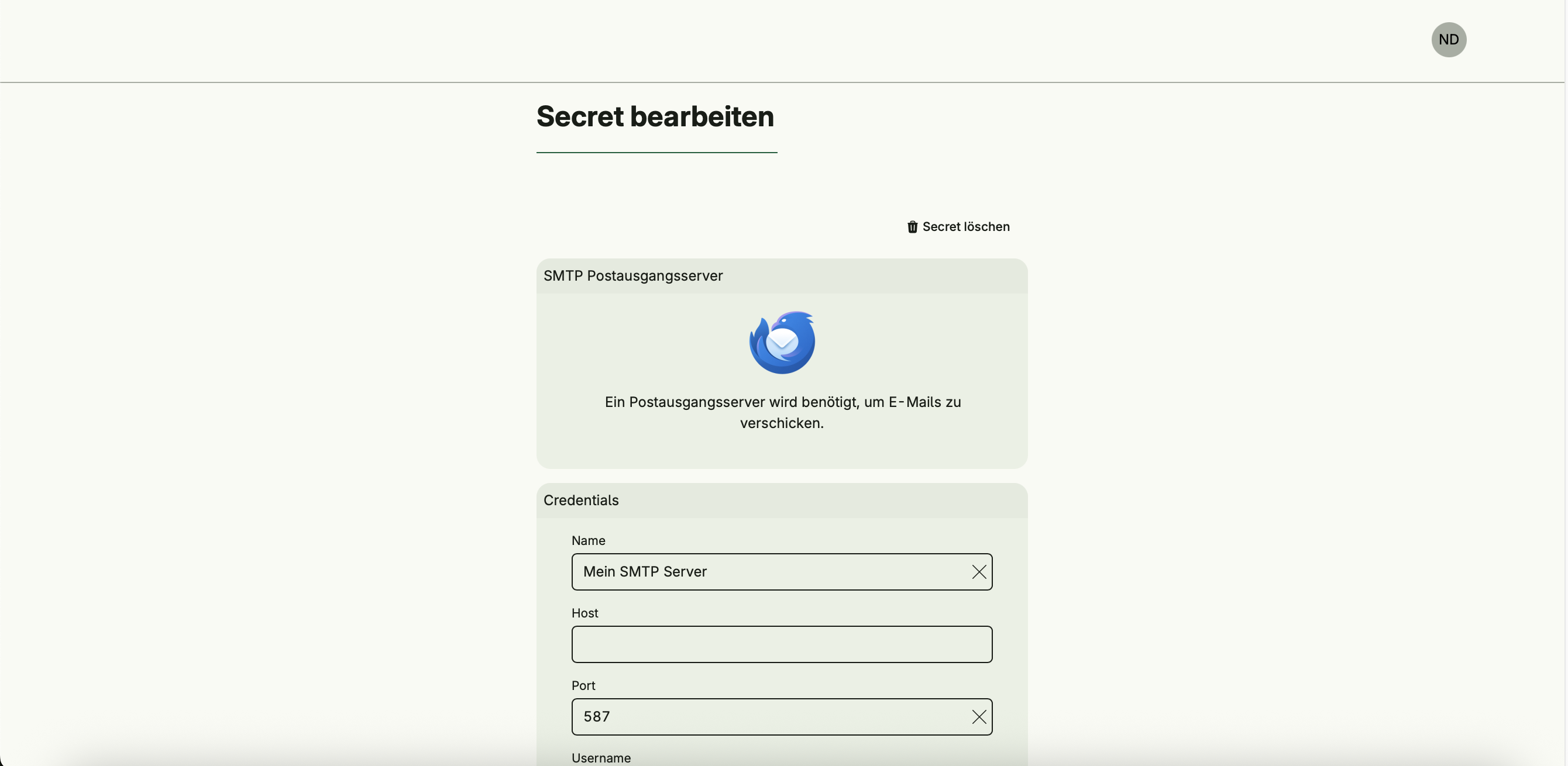
- SMTP Server – Required for sending emails. It must be associated with the
systemgroup, and the user creating it must also belong to this group.
package secret
var _ = enum.Variant[Credentials, SMTP]()
type SMTP struct {
Name string `value:"Mein SMTP Server"`
Host string
Port int `value:"587"`
Username string
Password string `style:"secret"`
_ string `credentialName:"SMTP Postausgangsserver" credentialDescription:"Ein Postausgangsserver wird benötigt, um E-Mails zu verschicken." credentialLogo:"https://www.thunderbird.net/media/img/thunderbird/favicon-196.png"`
}
func (SMTP) Credentials() bool {
return true
}
func (s SMTP) GetName() string {
return s.Name
}
func (s SMTP) IsZero() bool {
return s == SMTP{}
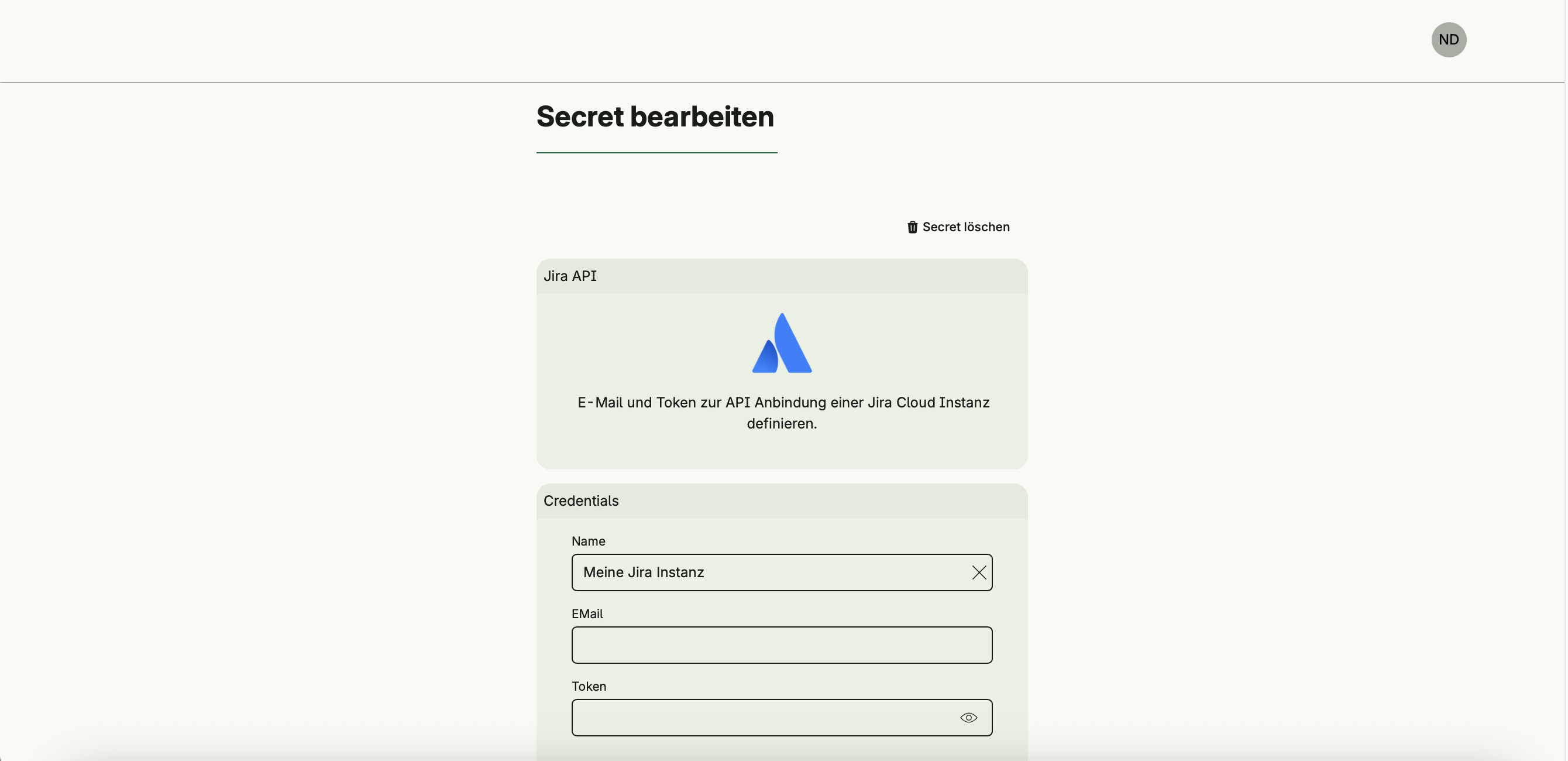
}- Jira API Token – Used to integrate with Jira Cloud via email and token.
package secret
var _ = enum.Variant[Credentials, Jira]()
type Jira struct {
Name string `value:"Meine Jira Instanz"`
EMail string
Token string `style:"secret"`
_ string `credentialName:"Jira API" credentialDescription:"E-Mail und Token zur API Anbindung einer Jira Cloud Instanz definieren." credentialLogo:"https://wac-cdn.atlassian.com/assets/img/favicons/atlassian/mstile-144x144.png"`
}
func (Jira) Credentials() bool {
return true
}
func (s Jira) GetName() string {
return s.Name
}
func (s Jira) IsZero() bool {
return s == Jira{}
}Each struct field leads to an input field. Developers can use tags to define special UI behaviour e.g. value, style etc.
Special characteristics
- Secrets can be shared to specific users and groups
- Secrets shared to users making them available in their secret store
- Secrets shared in groups making them available to all members of those groups for relevant use cases but not visible in their secret store
- The SMTP secret type is implemented by default and already available after activating the Secret Management
Dependencies
Requires:
If these are not already active, they will be enabled automatically when Secret Management is activated.
Is required by:
- Mail Management – for storing SMTP configuration.
Activation
This system is activated via the configurator:
std.Must(cfg.SecretManagement())secretManagement := std.Must(cfg.SecretManagement())