Session Management
The Session Management system is responsible for handling user sessions, including login, logout, authentication state, and session expiration.
Furthermore, it integrates login via Single Sign-On (SSO).
It is automatically initialized when the application starts and is therefore always active.
The available use cases can also be consumed programmatically if needed.
Functional areas
Session Management provides the following key functions:
Session lifecycle
- Create and manage user sessions
- Identification via a unique session ID (cookie-based)
- Manage session expiration (default: 3 months after last authentication)
- Clear all sessions if necessary (e.g., for debugging or recovery)
Authentication
- Login via email and password
- Login via Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Logout and invalidate a session
User sessions
- Access persistent session information of a client (
UserSession) - Store and retrieve session-specific data via key-value pairs
- Track authentication and creation timestamps
Example: Usage of the session storage
cfg.RootViewWithDecoration("first_page", func(wnd core.Window) core.View {
textState := core.AutoState[string](wnd)
return ui.VStack(
ui.Text("Enter some information:"),
ui.TextField("Information", textState.Get()).InputValue(textState),
ui.PrimaryButton(func() {
// Store the text into the session
if err := wnd.Session().PutString("user_info", textState.Get()); err != nil {
alert.ShowBannerError(wnd, fmt.Errorf("failed to store session value: %w", err))
return
}
// Navigate to the second page
wnd.Navigation().ForwardTo("second_page", nil)
}).Title("Continue"),
).Gap(ui.L24).Frame(ui.Frame{}.MatchScreen())
})cfg.RootViewWithDecoration("second_page", func(wnd core.Window) core.View {
// Retrieve stored information from the session
info, ok := wnd.Session().GetString("user_info")
return ui.VStack(
ui.IfElse(ok,
ui.Text(fmt.Sprintf("Stored information: %s", info)),
ui.Text("No information found in session"),
),
ui.PrimaryButton(func() {
// Go back to the first page
wnd.Navigation().Back()
}).Title("Go Back"),
).Gap(ui.L24).Frame(ui.Frame{}.MatchScreen())
})Single Sign-On (SSO)
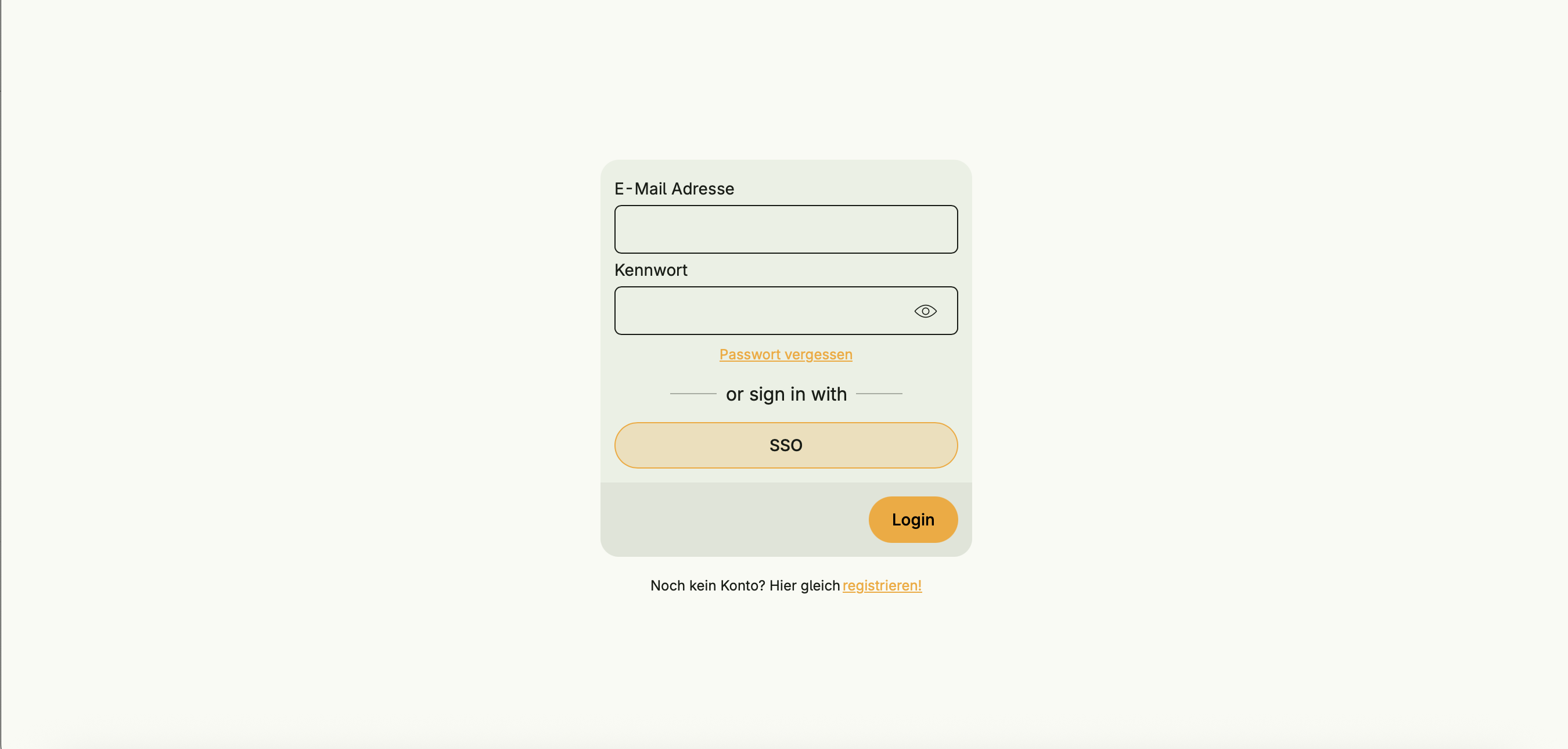
Through the integrated Nago Login Service (NLS), users can also log in via SSO:
StartNLSFlow: initializes the login process and returns a redirect URLExchangeNLS: exchanges a nonce for a refresh tokenRefreshNLS: updates a session using the refresh token- Seamless integration with User Management (merge/update of SSO users)
Currently, only Microsoft Entra ID is supported as an external provider.
Support for additional common SSO providers (e.g. Google) is planned in the future.
Configuration via Settings Management
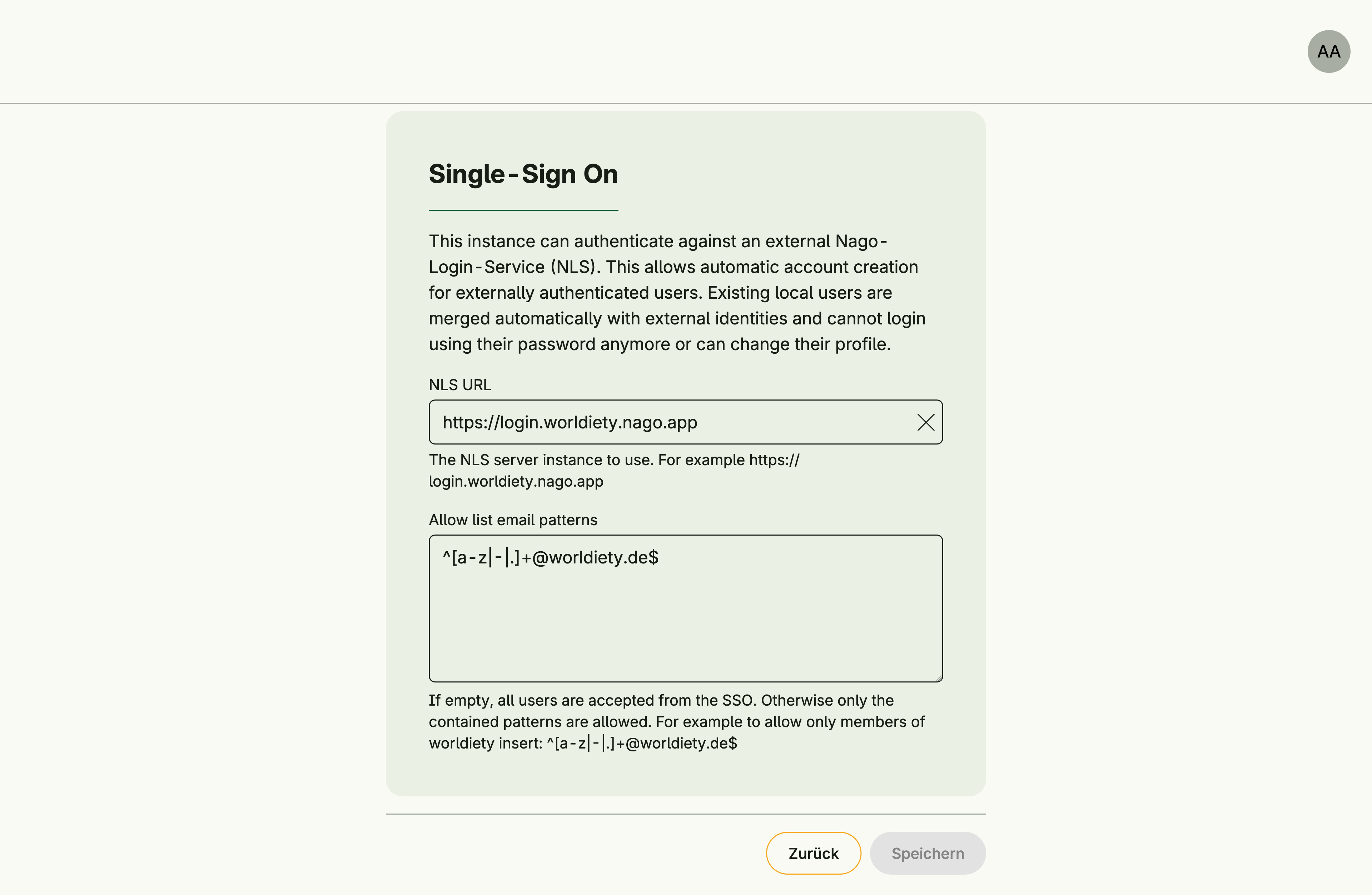
SSO must be enabled and configured in Settings Management:
- NLS URL: The NLS server instance to use.
Example:https://login.worldiety.nago.app - Allow list email patterns:
If empty, all users are accepted from the SSO.
Otherwise, only users with matching email patterns are allowed.
Example: to allow only members of worldiety:^[a-z|-|.]+@worldiety.de$
Code usage
Example: finding a user session and checking its authentication state.
import (
"go.wdy.de/nago/application/session"
"go.wdy.de/nago/pkg/std"
"log/slog"
)
func checkSession(sessionManagement session.UseCases, id session.ID) {
s, err := sessionManagement.FindSessionByID(id)
if err != nil {
slog.Error("failed to load session", slog.Any("error", err))
return
}
if s.IsNone() {
slog.Info("session expired or not found")
return
}
userSession := s.Unwrap()
if userSession.User.IsNone() {
slog.Info("session exists but is not authenticated")
return
}
slog.Info("active session for user", slog.Any("userID", userSession.User))
}Dependencies
Requires:
If these are not already active, they will be enabled automatically when Session Management is activated.
Is required by:
- none
Run().Activation
This system is activated via:
std.Must(cfg.SessionManagement())sessionManagement := std.Must(cfg.SessionManagement())