Token Management
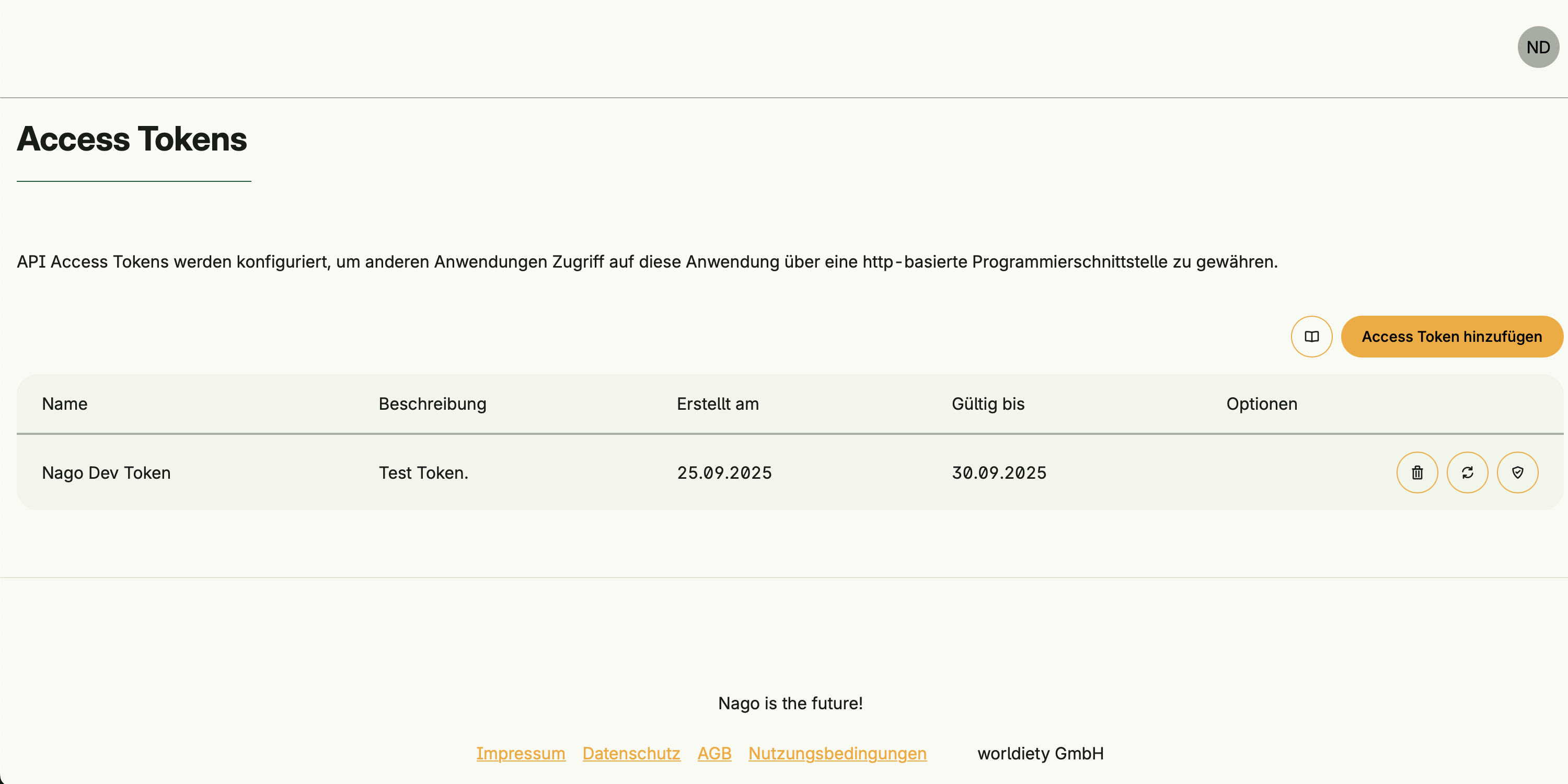
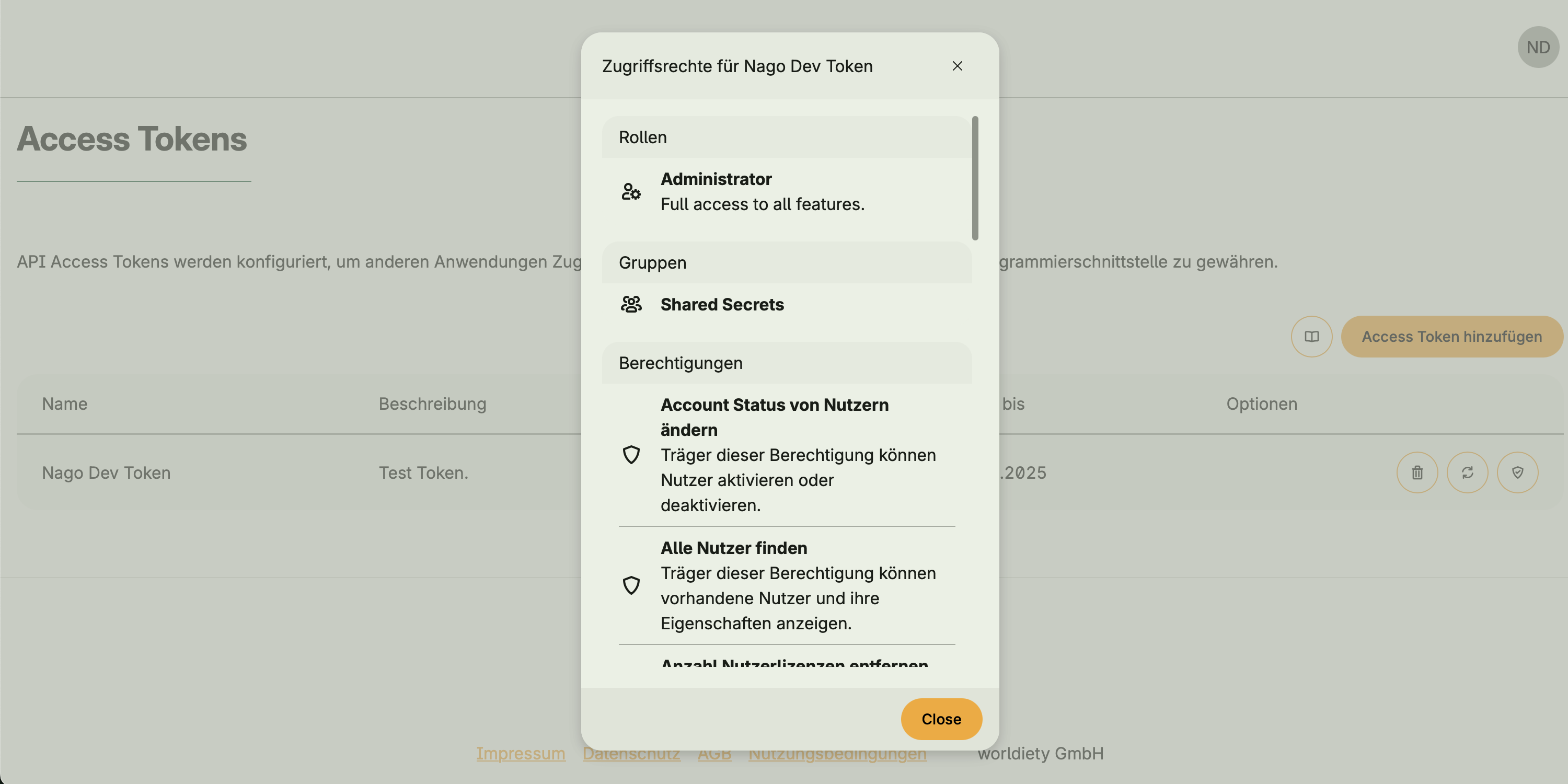
Token Management provides the ability to create and manage API access tokens.
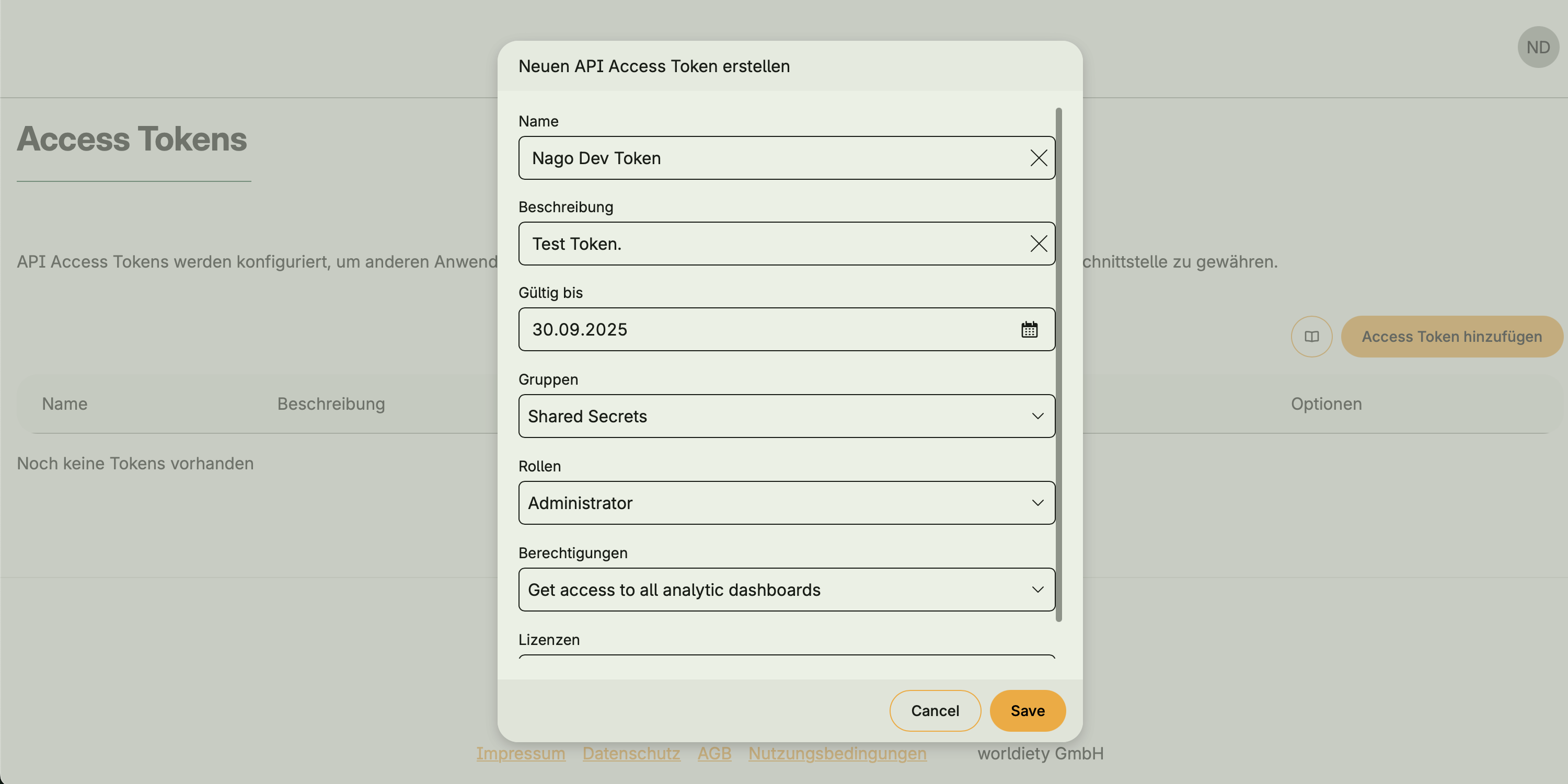
Tokens act like users: they can have groups, roles, permissions, and licenses assigned.
This allows external applications or users to authenticate against the system and gain access to defined resources.
ℹ️
Tokens are primarily intended to be used with HAPI Management.
While APIs can also be exposed without authentication, Token Management enables secure and fine-grained access control.
While APIs can also be exposed without authentication, Token Management enables secure and fine-grained access control.
Functional areas
Token Management provides the following key functions:
Token creation and editing
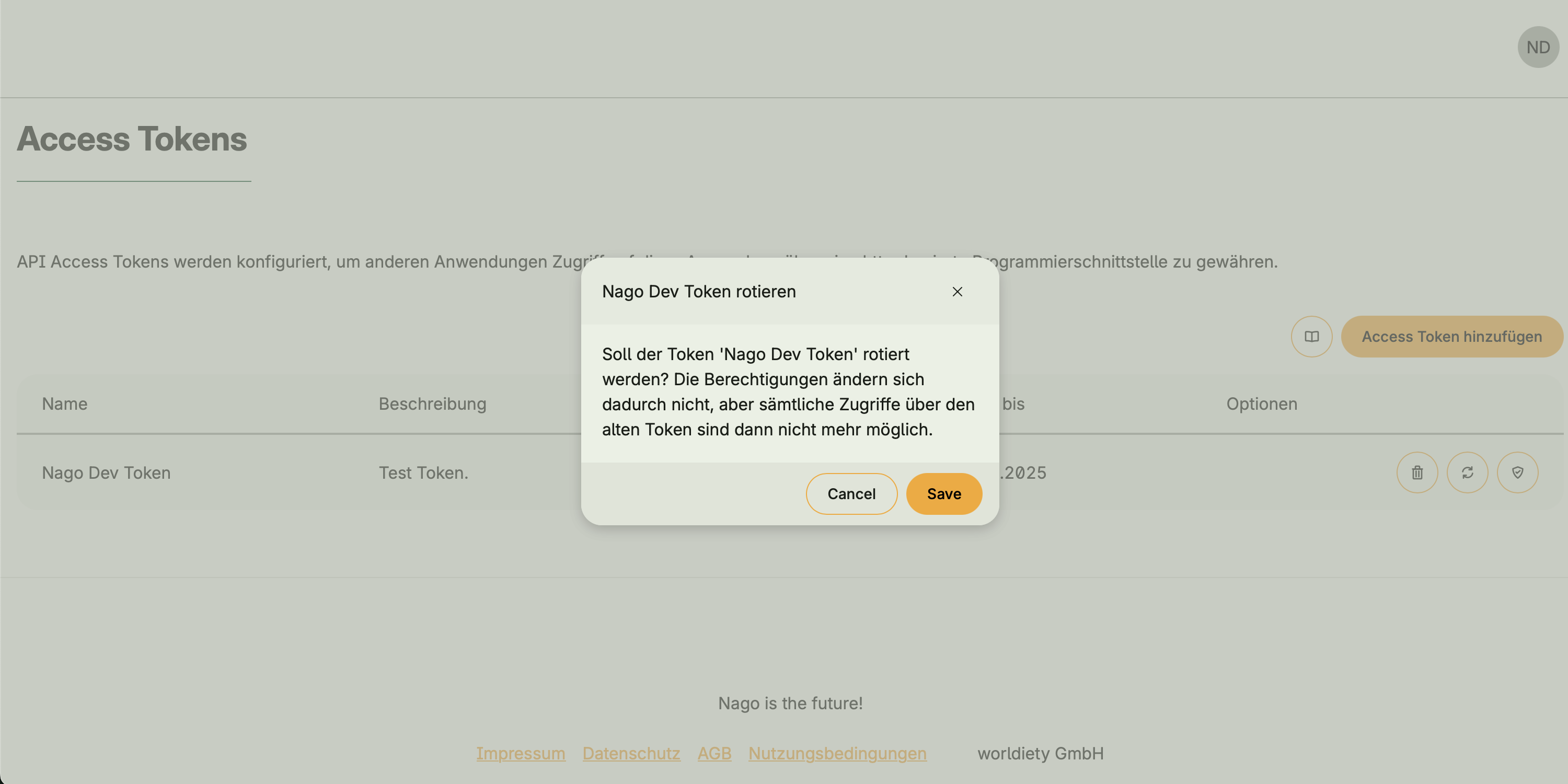
- Create, rotate, and delete tokens
- Assign groups, roles, permissions, and licenses
- Define token validity (expiration date)
⚠️
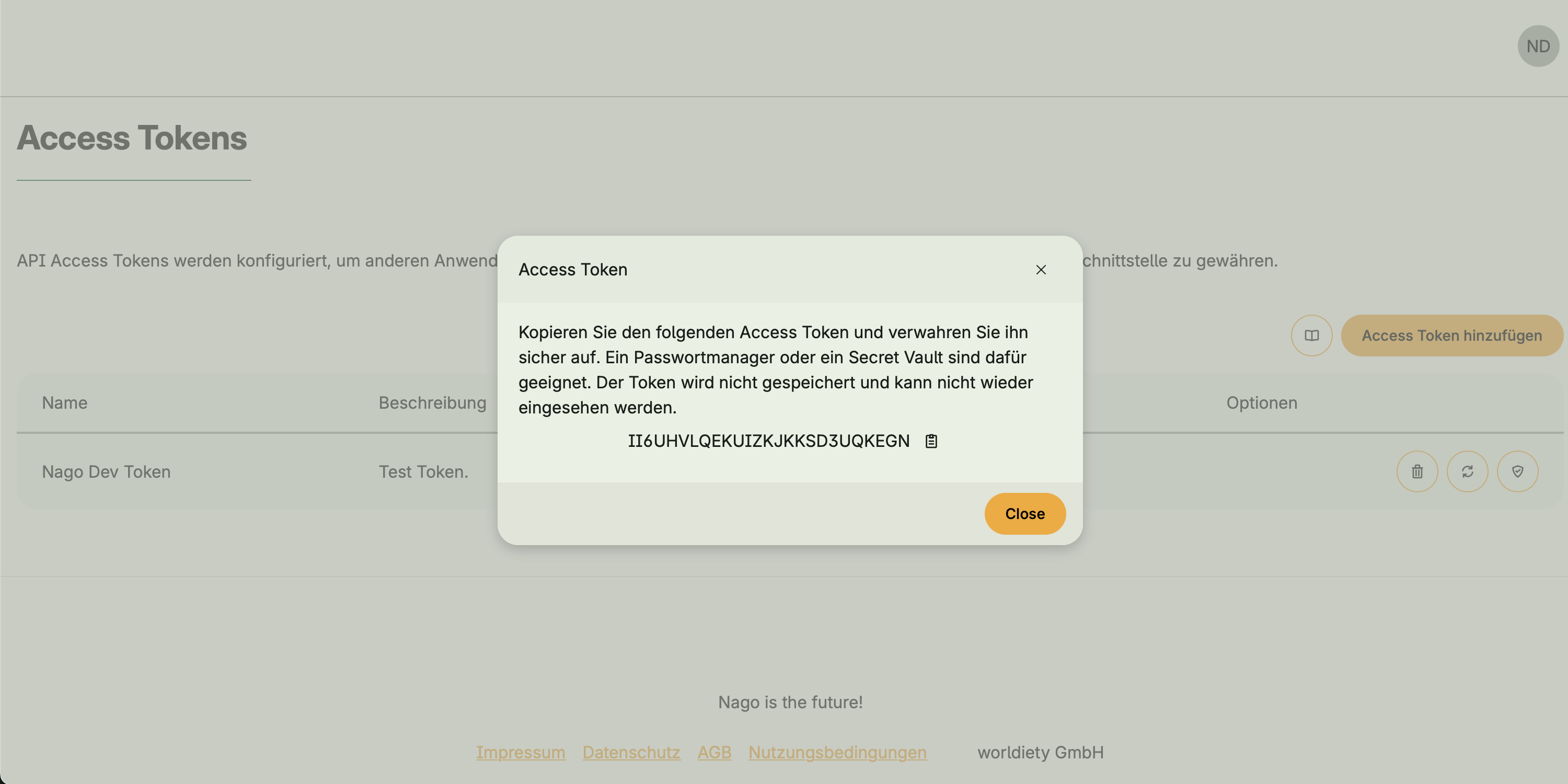
The plaintext token is only shown once during creation!
Make sure to copy and securely store it immediately.
After closing the dialog, the token cannot be viewed again – only rotated or deleted.
Make sure to copy and securely store it immediately.
After closing the dialog, the token cannot be viewed again – only rotated or deleted.
Example: API Authentication
The most common integration is authenticating API calls with a bearer token.
hapi.Get[SomeRequest](api, hapi.Operation{Path: "/api/v1/protected"}).
Request(
hapi.BearerAuth[SomeRequest](tokens.UseCases.AuthenticateSubject, func(dst *SomeRequest, subject auth.Subject) error {
dst.Subject = subject
return nil
}),
).
Response(
hapi.ToJSON[SomeRequest, SomeResponse](func(in SomeRequest) (SomeResponse, error) {
return SomeResponse{Message: "Access granted for " + in.Subject.ID()}, nil
}),
)With this setup:
- A client includes the token in the Authorization: Bearer
header - Token Management validates the token and injects the authenticated auth.Subject
- The API can enforce access control based on the subject’s roles, groups, and permissions
Dependencies
Requires:
If these are not already active, they will be enabled automatically when Token Management is activated.
Is required by:
- none
Activation
This system is activated via:
std.Must(cfg.TokenManagement())tokenManagement := std.Must(cfg.TokenManagement())